How to Identify Fake Websites and Online Scams
Easy life, but complicated in some cases for those people who have taken cybercrime. The scope of having fake websites and online scams has very much increased since phishing to online store counterfeit. Money is scammed with the help of malware download or by leading people to give their personal details and pay.
Protecting your finances, personal data, and digital security would need you to learn the difference between genuine and fraudulent websites. In this guide, we will look at certain helpful hints on how to recognize fraudulent websites, common online scams, and how you can be safe while browsing.
1. Understanding Fake Websites and Online Scams
1.1 What Are Fake Websites?
Fake websites are fraudulent sites that are created to represent legitimate businesses such as banks, social media and ecommerce sites, and other related sites on the web to steal personal information, such as usernames and passwords for logging in as well as payment information. Some fake websites will spread malware while others might just fool the victims into thinking that they are selling a product which is never delivered.
1.2 Common Online Scams
Scammers used several modalities to trick users online. Some of causes of online scams are:
Phishing Scam – Fake websites are designed to help steal credentials by cloning the login pages of banks, social web providers, or even email providers.
Fake E-commerce Stores – Sites that sell goods at unbelievably ridiculous prices so as to lure customers but will never ship the required goods.
Tech Support Scam – As a pop-up, it would state that your machine has a virus and request you to call their support number to fix it, hence it cannot help at all to solve your problem with your PC.
Lottery and Prize Scams – Nonexistent award agencies, proposing that you have won a prize, yet is needing you to first pay some "administration fee" before you can claim it.
Investment Scams: Single fake platforms for investing your money in cryptocurrency, forex trading, or stock making promises of high return against minimal or no risk at all.
Knowing these scams will help you in making sure that you can identify the red flags regarding these scams before you yourself become a victim.
2. Identify a Fake Website
2.1 Check The Website URL
A URL can say so much about a given site, including if or not it is legitimate. The following signs help you tell a difference:
Misspelled domain names : The fraudulent ones create domains that look somewhat similar to the ones converted (e.g.’ "amaz0n.com", instead of "amazon.com").
Extra words or symbols- it generally has added words such as "paypal-security.com," whereas noted before as "paypal.com."
An unusual domain extension- Most legitimate business websites will carry a legitimate extension such as .com, .org, or .net. Whereas its fraudulent counterpart will use domains such as .xyz, .top, or .info.
Check Using The Following Method:
Hover over a link before clicking it to see what the real URL is.
Type the URL in the browser rather than clicking links in an email or message.
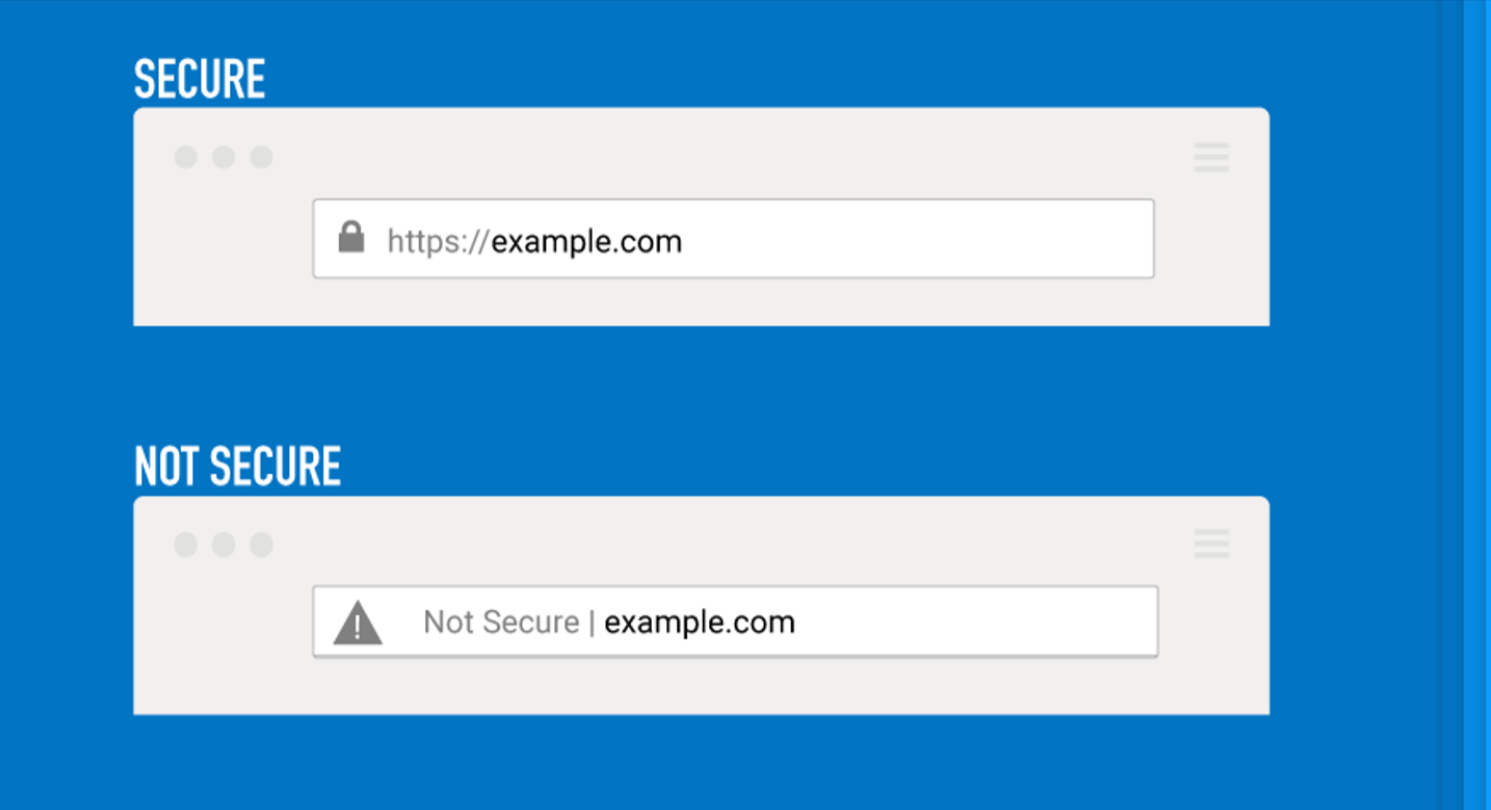
2.2 Look for HTTPS along with SSL Certificate
Secure websites typically transmit HTTPS traffic, which means they encrypt data to protect users as opposed to doing so at sending HTTP data over unsecured transmission. However, it's not always safe to assume that an HTTPS site is a safe one, because that is also how some scammers use SSL.
To check:
Click on the padlock icon and check the certificate details next to the URL.
A legitimate business is expected to have Extended Validation (EV) certificate showing the legal name of the business entity.
Be wary of any website that has only HTTPS but no other indications of legitimacy.
2.3 Investigate The Website's Design And Content
Many fake sites have very bad design, incorrect grammar, and poor quality images. Signs that a website may be fraudulent:
Poorly written content with grammar errors and misspellings
Low-quality logos, images appearing blurry
Branding is inconsistent - Compare this to the official website of the company.
2.4 Verify Contact Information
Usually, they provide contact details about real sites. Fake websites often provide vague or no contact information.
How to check:
Search for the physical address in Google Maps.
Call the customer support number to check it out for yourself.
Send an email and see if reply comes from a company domain email (not from some mail service such as Gmail or Yahoo).
Fake websites usually list non-existent phone numbers or addresses to seem to have legitimacy.
2.5 Search for Online Reviews
Before using a particular website, see what other users have to say.
For the checking;
Search for "[website name] scam" or "[website name] reviews" on Google.
See if there are any indications about the website on Trustpilot, the better business bureau, or discussions on Reddit.
Be careful of fake reviews- if all of them sound too positive or too generic, they might be fake.
2.6 Realistic Offers Should Raise Red Flags
If the site sells products for incredibly low prices, it is clearly a scam.
Red flag includes:
Too substantial discounts to be true.
Limited time offer pressures you to hurry and buy.
No avenue for customer support to address inquiries.
If it is too good to be true, it usually is.
3. Identify the Online Scams
3.1 Identification of Phishing Emails
A scammer would send a phishing email with a fake link on it to acquire login credentials.
Some signs of phishing emails:
Generic greetings, such as "Dear User" instead of your name.
A claiming "act now or your account will be locked" urgent message.
Attachment or link gets into personal information.
How to check it:
Hover over links for viewing the real URL prior to clicking.
For safety, contact the company directly if you are unsure.
3.2 Avoid Fake Online Shops
To check if an online store is real:
There should be an actual secure payment mechanism such as PayPal or credit cards (avoid bank transfers).
Describes returns in its terms and gives a clear customer service contact point.
Domain age verification using tools like Whois Lookup-fake stores mostly have a newly registered domain.
3.3 Job Scam Identification
Fraudsters issue different fake job advertisements to lure people and obtain personal information.
Signs for Everyone to Be Aware About:
Very high salary for little work.
Application procedure that requires advance fees.
No free company domain email account.
Research, research your company before applying.
4. How to Stay Safe Online
4.1 Check If the Site Is Safe Using Verification Tools
Before giving any personal information, visit these tools to check the site security:
Google Transparency Report
Scamadviser
Whois Lookup
4.2 Enable Two Factor Authentication
2FA will keep your password safe when it is stolen. Simply do:
Email accounts Online Banking and Shopping websites
Social networking sites
4.3 Don't save up payment information in any untrusted sites
Never save credit card information on unknown sites. Whenever possible, use:
Virtual credit cards PayPal or Apple Pay other than providing card information directly
4.4 Have regular updates of security programs or browsers
In the same vein, as new threats, so are the security software and browser updated. There is:
Ad blockers for those unsolicited popups;
Antivirus programs such as Norton, Bitdefender, or Malwarebytes will protect you.
Conclusions
Fake websites and online scams exist everywhere, but how they can be identified allows individuals to save their personal details, finances, and safety online.
Ensure you have always cross-checked U-R-Ls, link with credible security websites, and avoid offers that are too good to be true.
Abide by the guide rules elaborated: check domain names, check for secure HTTPS connection, avoid phishing emails, and use verification tools. That will enable you to surf freely and avoid such online scams.